Infrared Thermometer
Introduction to Non contact Infrared Thermometers
On its most basic design an infrared sensor consists of a lens to focus the infrared (IR) energy on to a detector, which
converts the energy to an electrical signal that can be displayed in units of temperature after being compensated for ambient temperature variation.
This configuration facilitates temperature measurement from a distance without contact with the object to be measured (non-contact temperature measurement). As such, the infrared
thermometer is useful for measuring temperature under circumstances where thermocouples or other probe type sensors cannot be used or do not
produce accurate data for a variety of reasons.
Some typical circumstances are where the object to be measured is moving; where the object
is surrounded by an EM field, as in induction heating; where the object is contained in a vacuum or other controlled atmosphere; or in
applications where a fast response is required.
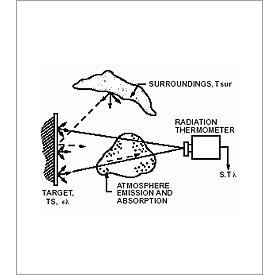
Noncontact Temperature Measurement
Learn more about Infrared Thermometers
Why should I use an infrared thermometer to measure temperature in my application?
Non-contact pyrometers allow users to measure temperature in applications where conventional sensors cannot be employed. Specifically,
in cases dealing with moving objects ( i.e., rollers, moving machinery, or a conveyor belt), or where non-contact measurements are
required because of contamination or hazardous reasons (such as high voltage), where distances are too great, or where the temperatures
to be measured are too high for thermocouples or other contact sensors.
How to Choose an Infrared Thermometer
- Determine the field of view (target size and distance)
- Consider the type of surface being measured and its emissivity
- Analyze the spectral response for atmospheric effects or transmission through surfaces
- Specify the temperature range and the mounting needs
- Don't forget: response time, environment, mounting limitations, viewing port or window applications, and desired signal processing
What should I consider about my application when selecting an IR thermometer?
The critical considerations for any infrared pyrometer include field of view (target size and distance), type of surface being measured
(emissivity considerations), spectral response (for atmospheric effects or transmission through surfaces), temperature range and mounting
(handheld portable or fixed mount). Other considerations include response time, environment, mounting limitations, viewing port or window
applications, and desired signal processing.
What is meant by Field of View, and why is it important?
The field of view is the angle of vision at which the instrument operates, and is determined by the optics of the sensor. To obtain an accurate
temperature reading, the target being measured should completely fill the field of view of the instrument. Since the infrared device determines
the average temperature of all surfaces within the field of view, if the background temperature is different from the object temperature,
a measurement error can occur. OMEGA offers a unique solution to this problem. Many OMEGA infrared pyrometers feature patented laser switchable
from circle to dot. In the circle mode a built-in laser sighting creates a 12-point circle which clearly indicates the target area being measured.
In the dot mode a single laser dot marks the center of the measurement area.
Choose the right Infrared for your application
 Infrared Thermometer Gun
Infrared Thermometer Gun
A handheld infrared thermometer is one of the most popular type
of infrared pyrometer. They are commonly used for portable applications although some models also feature an integral tripod mount. OMEGA
offers a large variety of infrared thermometers in various shapes and form factors. Many of OMEGA pyrometers feature OMEGA's patented Circle Dot/Circle Laser thermometer which clearly outlines the field of view of the gun.
 Two Color-Ratio Thermometry
Two Color-Ratio Thermometry
Given that emissivity plays such a vital role in obtaining accurate temperature data from infrared thermometers, it is not surprising that
attempts have been made to design sensors which would measure independently of this variable. The best known and most commonly applied of
these designs is the Two Color-Ratio Thermometer. This technique is not
dissimilar to the infrared thermometers described so far, but
measures the ratio of infrared energy emitted from the material at two wavelengths, rather than the absolute energy at one wavelength or
wave band. The use of the word "color" in this context is somewhat outdated, but nevertheless has not been superseded. It originates
in the old practice of relating visible color to temperature, hence "color temperature."
Frequently Asked Questions
What is emissivity, and how is it related to infrared temperature measurements?
Emissivity is defined as the ratio of the energy radiated by an object at a given temperature to the energy emitted by a perfect radiator,
or blackbody, at the same temperature. The emissivity of a blackbody is 1.0. All values of emissivity fall between 0.0 and 1.0. Most infrared
thermometers have the ability to compensate for different emissivity values, for different materials. In general, the higher the emissivity of
an object, the easier it is to obtain an accurate temperature measurement using infrared. Objects with very low emissivities (below 0.2) can be
difficult applications. Some polished, shiny metallic surfaces, such as aluminum, are so reflective in the infrared that accurate temperature
measurements are not always possible.
Five Ways to Determine Emissivity
There are five ways to determine the emissivity of the material, to ensure accurate temperature measurements:
- Heat a sample of the material to a known temperature, using a precise sensor, and measure the temperature using the IR instrument.
Then adjust the emissivity value to force the indicator to display the correct temperature.
- For relatively low temperatures (up to 500°F), a piece of masking tape, with an emissivity of 0.95, can be measured. Then adjust the
emissivity value to force the indicator to display the correct temperature of the material.
For high temperature measurements, a hole (depth of which is at least 6 times the diameter) can be drilled into the object.
- This hole acts as a blackbody with emissivity of 1.0. Measure the temperature in the hole, then adjust the emissivity to force the
indicator to display the correct temperature of the material.
- If the material, or a portion of it, can be coated, a dull black paint will have an emissivity of approx. 1.0. Measure the
temperature of the paint, then adjust the emissivity to force the indicator to display the correct temperature.
- Standardized emissivity values for most materials are available (see pages 114-115). These can be entered into the instrument
to estimate the material's emissivity value.
How can I mount the infrared pyrometer?
The pyrometer can be of two types, either fixed-mount or portable. Fixed mount units are generally installed in one location to
continuously monitor a given process. They usually operate on line power, and are aimed at a single point. The output from this type
of instrument can be a local or remote display, along with an analog output that can be used for another display or control loop.
Battery powered, portable infrared ''guns'' are also available; these units have all the features of the fixed mount devices, usually
without the analog output for control purposes. Generally these units are utilized in maintenance, diagnostics, quality control,
and spot measurements of critical processes.
How is a infrared pyrometer calibrated?
There are basically two types of infrared calibration sources, hot plate blackbody source and cavity type blackbody source. The hot plate style consists of a metal plate (usually aluminium) with or without concentric grooves where the temperature of the-plate is set and controlled using either an inexpensive potentiometer dial or a high-end temperature controller. The temperature of the plate is sensed using either a thermocouple or an RTD probe. The hot plate is usually painted dull black to improve the surface emissivity. The surface emissivity of a hot plate calibration source is typically 0.95.
 OMEGA's BB703 Model
OMEGA's BB703 Model is a high-end hot plate blackbody source with a built-in temperature controller. The calibration source with built-in temperature controller has much better accuracy and stability compared to a potentiometer dial type unit.
The cavity type blackbody source consists of a blind hole in a cylinder or a sphere where the temperature of the cavity is controlled by a temperature controller, using a thermocouple probe. The cavity type blackbody source has a higher surface emissivity than a hot plate blackbody unit. The emissivity of a cavity type blackbody source is typically 0.98 or higher.
The
OMEGA's BB705 Model cavity type blackbody typically goes to higher temperatures (over 530°C [1000°F]) than hot plate blackbodies. In addition, having a higher emissivity value makes them ideal for precise calibration tasks.
In order to calibrate an infrared thermometer, a blackbody calibration source is required. There are 3 factors to consider when selecting a blackbody calibration source:
- Type of blackbody (hot plate or cavity type) tells us about the construction and overall performance of the unit.
- Target area tells us how large of an area we can check our infrared thermometers with. The target area should be larger than the field of view of the thermometer; otherwise the infrared thermometer will be measuring the target area plus some of the surrounding cooler areas. Normally, an infrared thermometer is checked against a blackbody source at a relatively close distance (about 0.15 to 1m), depending on the target area).
- The higher the target emissivity, the more ideal is the calibration. At lower emissivity targets, wavelength bandwidth of the infrared thermometer comes into play. Ideally at E=1.00, wavelength bandwidth of the DUT (Device Under Test) is not a factor.
Infrared | Related Products
↓ View this page in another language or region ↓
 CLOSE
CLOSE















 Thermomètre Infrarouge
Thermomètre Infrarouge Termómetros Infrarrojos
Termómetros Infrarrojos Termómetros Infrarrojos
Termómetros Infrarrojos Infrared Thermometer
Infrared Thermometer Infrarøde Termometre
Infrarøde Termometre Thermomètre Infrarouge
Thermomètre Infrarouge Infrarot-Temperaturmessgeräte
Infrarot-Temperaturmessgeräte Termometri ad Infrarosso
Termometri ad Infrarosso Infrared Thermometers
Infrared Thermometers Termómetro Infrarrojo
Termómetro Infrarrojo Infrared Thermometer
Infrared Thermometer Infrared Thermometers
Infrared Thermometers 红外温度计
红外温度计 Infrared Thermometers
Infrared Thermometers
 赤外線温度計
赤外線温度計 적외선 온도계
적외선 온도계 Infrared Thermometers
Infrared Thermometers
 Infrared Thermometers
Infrared Thermometers
 Infrared Thermometers
Infrared Thermometers
 Infrared Thermometers
Infrared Thermometers
 Infrared Thermometers
Infrared Thermometers